The IMO
The structure and governing body of the IMO are designed to ensure that proposed legislation and ambitions are grounded in a democratic system, where the interests of the member states can be presented and considered.
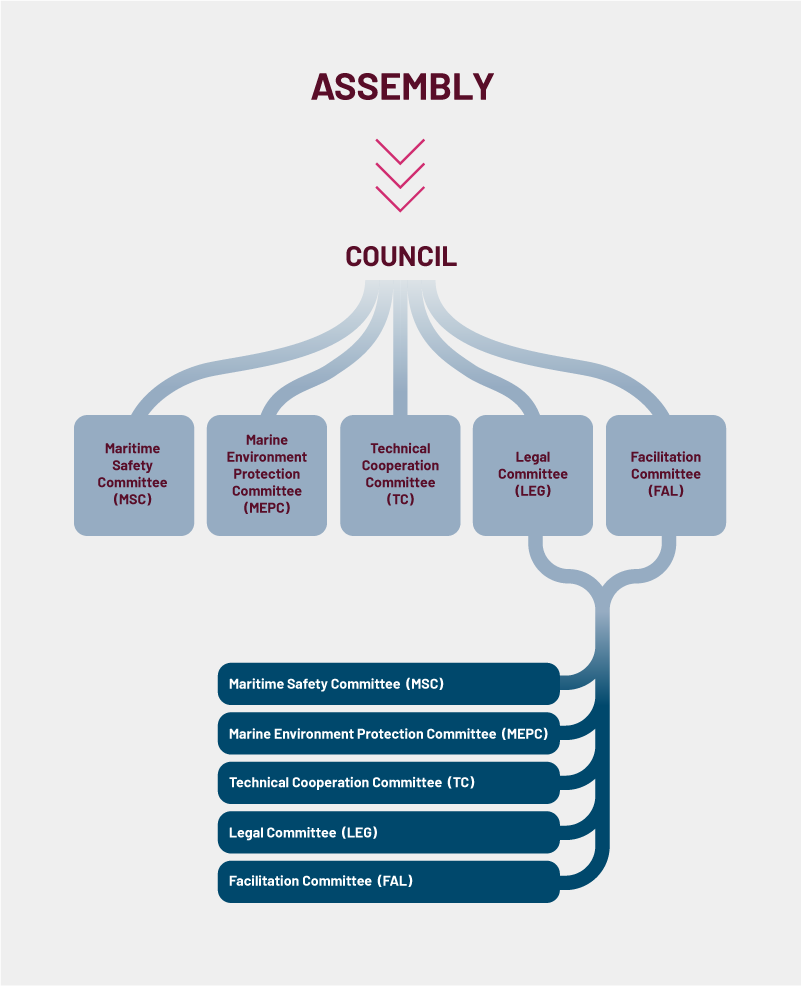
The IMO has 176 member states. They are all represented in the Assembly, which establishes the organisation's overall direction and budget every two years. The Council of the IMO comprises 40 member countries, elected by the Assembly. The Council oversees the IMOs work between the Assembly sessions, held every two years.
The IMO has several key committees that play a crucial role in developing and updating regulations and guidelines across various aspects of maritime safety, security, and environmental protection.
In these committees, member countries collaborate with relevant organisations. The structure of the IMO and its committees is shown below.
Learn more at IMO’s governing body.
FAQ the IMO
-
How is the IMO structured?
The IMO's structure consists of the Assembly, representing all member states, and the Council, comprised of 40 elected member countries. Additionally, specialized committees and subcommittees focus on various aspects of maritime regulation.
-
How many states are represented in the IMO?
There are 176 member states represented in the IMO.
-
What is the overall focus of the IMO?
The overall focus of the IMO is to protect the environment, improve safety, and foster technical cooperation and responsible, sustainable shipping practices worldwide.
-
What are the indicative checkpoints in the revised strategy?
The indicative checkpoints include reducing total annual international shipping GHG emissions by at least 20% by 2030 and 70% by 2040, relative to 2008 levels.
-
What are the candidate measures in the revised strategy?
Candidate measures include a basket of both technical and economic elements, such as a goal-based marine fuel standard and a maritime GHG emissions pricing mechanism. Both measures to be adopted in 2025.
-
What is the Global Fuel Standard?
The Global Fuel Standard is a proposed framework that requires reductions in greenhouse gas intensity in marine fuels.
-
What is the economic measure?
The economic measure refers to adding a price to carbon emissions.
-
What is the Council in the IMO?
The Council is a body within the IMO, comprised of 40 member countries elected by the Assembly, overseeing the IMO's activities between sessions.
-
Who is in the Council in the IMO?
The Council includes 10 countries with major interests in providing international shipping services (Category a), 10 countries with significant interests in the international trade of bulk commodities (Category b), and 20 countries with specific maritime interests for broad geographical representation (Category c).
-
How do organizations work with the IMO?
Organizations, including IGOs and NGOs in observer or consultative status, collaborate with member states in committees, contributing to the legislative process and maritime discussions.
-
What is the role of IGOs in the IMO?
IGOs, especially those from the maritime sector or with regional maritime interests, collaborate with the IMO and can significantly influence member states' opinions on marine environmental issues.
-
What is the role of NGOs in the IMO?
NGOs, despite not having voting rights, play a significant role in the law-making process through their contributions, collaborations, and indirect influence via member states.
-
How do Member States and organizations work together in the IMO?
Member States and organizations work together in committees, focusing on environmental protection, safety, and technical cooperation. NGOs and IGOs collaborate on issues of mutual interest and contribute to the IMO's discussions and legislative process.