What does “alternative fuels” mean in shipping?
A new generation of fuels is intended to serve as an alternative to conventional fuels and contribute to bringing the shipping sector to net zero.
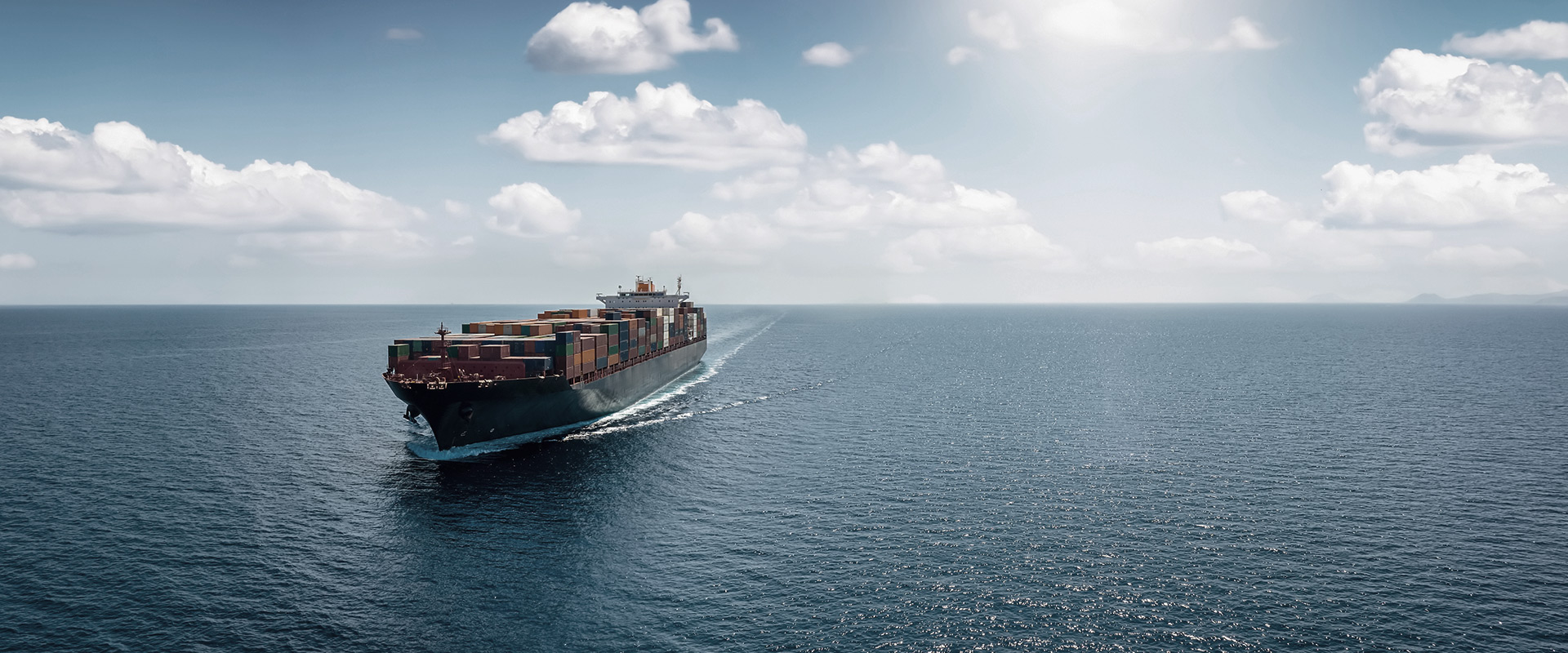
In shipping, 'alternative fuels' refer to energy sources that can replace traditional fossil fuels like heavy fuel oil (HFO) and marine diesel oil (MDO) used to power ships.
These alternative fuels produce lower emissions of pollutants like sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and carbon dioxide (CO2), which are major contributors to air pollution and climate change. The shipping industry is exploring alternative fuels to meet stricter environmental regulations and reduce its carbon footprint.
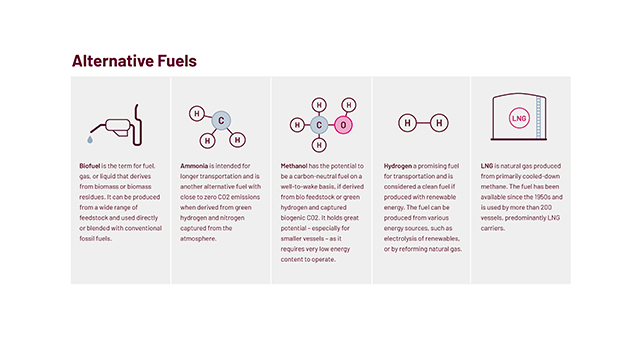
Some common examples of alternative fuels in shipping include:
1. Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)
2. Methanol
3. Biofuels
4. Ammonia
5. Hydrogen
6. Electricity. In some cases, ships can use batteries or shore power for operations in port, reducing reliance on traditional fuels. These alternatives are part of the shipping industry's effort to transition towards low-emission energy solutions.