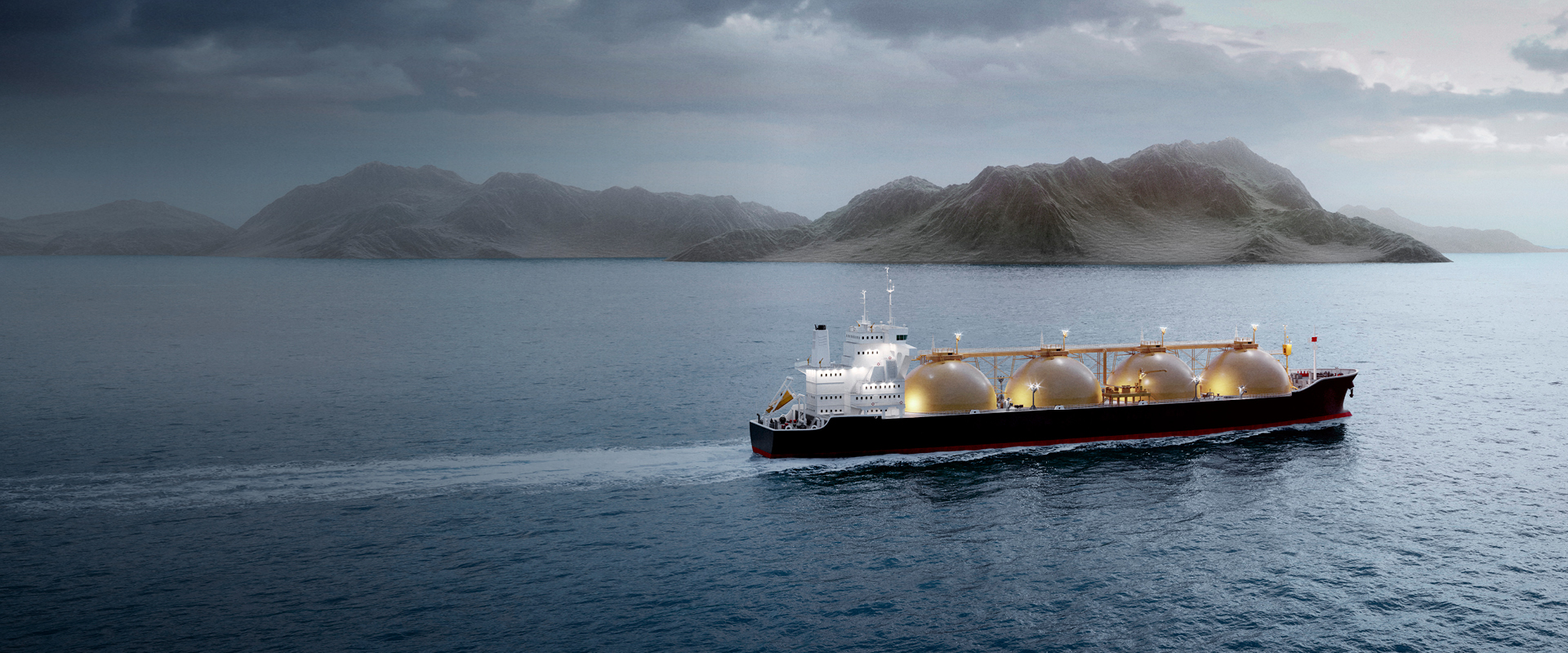
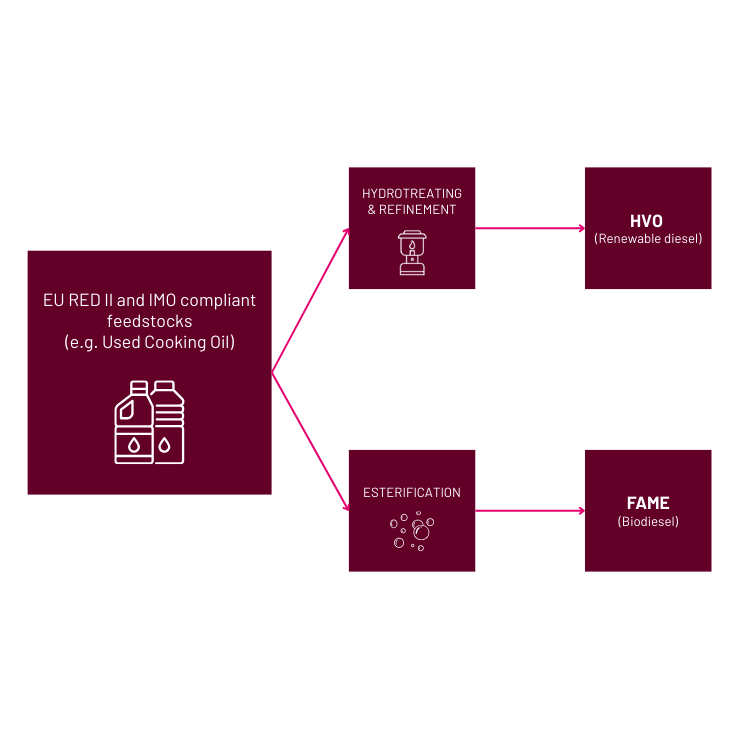
What is Fatty Acid Methyl Ester (FAME)?
FAME is produced from feedstocks like used cooking oil and animal fats, contributing to significant greenhouse gas emission reductions. It can reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by up 90%, possibly higher, depending on the feedstock used.
Its characteristics make it an attractive drop-in solution for operators looking to optimize their fuel strategies without requiring extensive modifications to existing ship engines.